
git merge
The "merge" command is used to integrate changes from another branch.
The target of this integration (i.e. the branch that receives changes) is always the currently checked out HEAD branch.
While Git can perform most integrations automatically, some changes will result in conflicts that have to be solved by the user. Read more about Dealing with Merge Conflicts in our online book.
Important Options
--no-ff
Creates a merge commit even when a fast-forward would be possible.
--squash
Combines all integrated changes into a single commit, instead of preserving them as individual commits.
--abort
When a conflict occurs, this option can be used to abort the merge and restore the project's state as it was before starting the merge.

The Git Cheat Sheet
No need to remember all those commands and parameters: get our popular "Git Cheat Sheet" - for free!
Usage Examples
Before using "git merge", make sure the correct local branch is checked out. Then, to perform the merge, simply specify which branch's commits you want to integrate:
git checkout develop
git merge feature/loginTip
Easy Branching & Merging in Tower
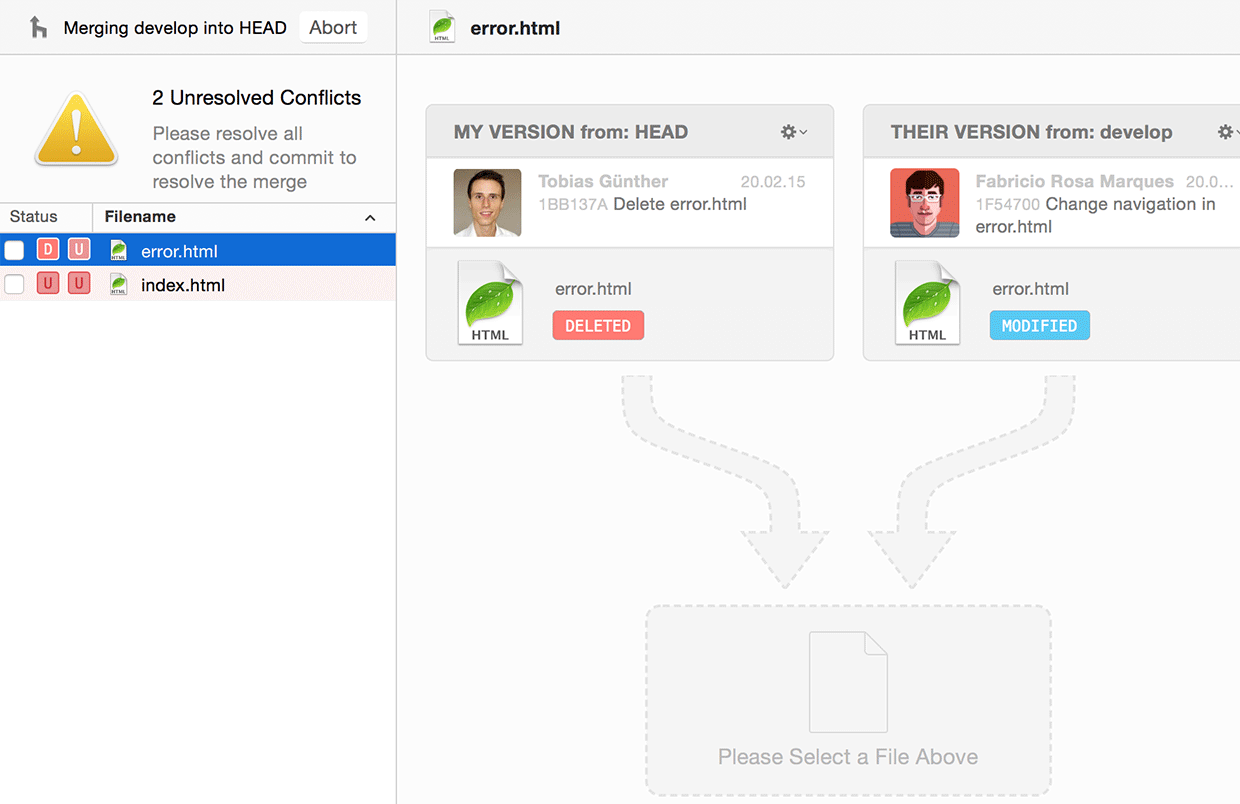
In case you are using the Tower Git client, merging branches is very easy: simply drag the branch you want to integrate and drop it onto your current HEAD branch in the sidebar.
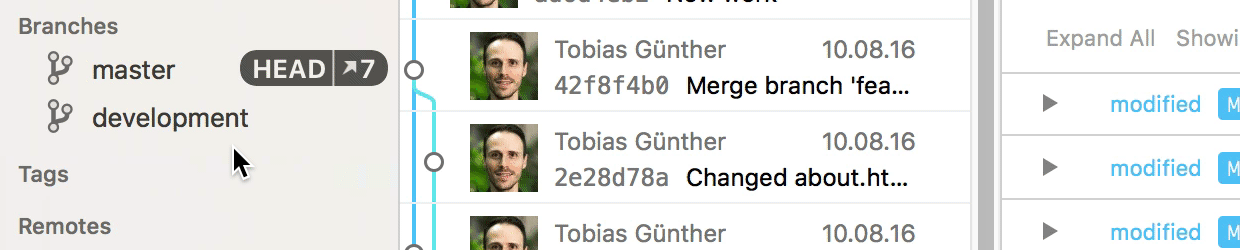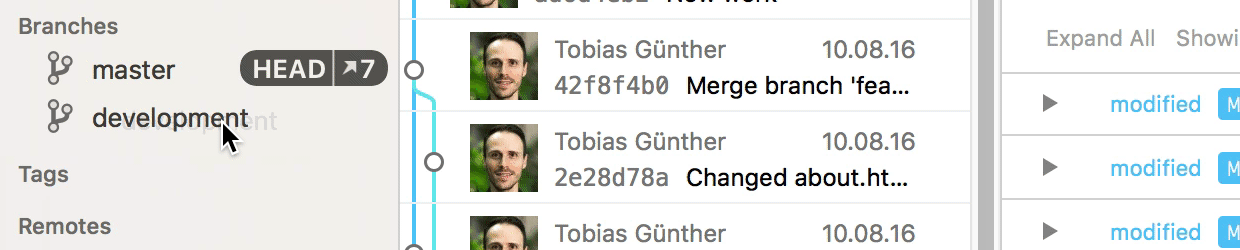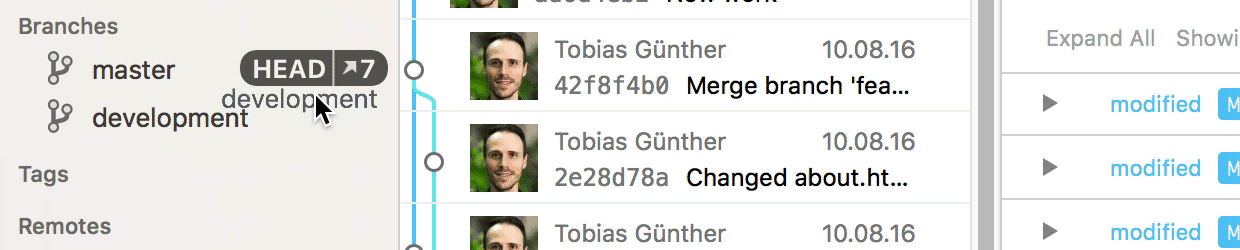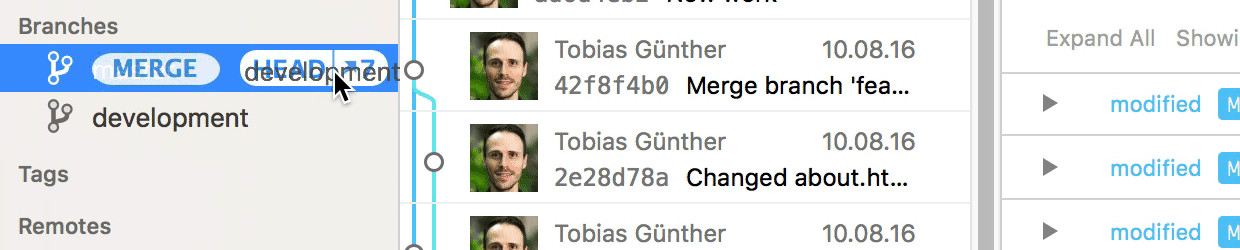
In case of a merge conflict, Tower's unique "Conflict Wizard" helps you solve the problems in an easy, visual way:
Learn More
- Check out the chapter Merging Changes in our free online book
- Find the full command description in the Git documentation
- More frequently asked questions about Git & version control
Get our popular Git Cheat Sheet for free!
You'll find the most important commands on the front and helpful best practice tips on the back. Over 100,000 developers have downloaded it to make Git a little bit easier.

About Us
As the makers of Tower, the best Git client for Mac and Windows, we help over 100,000 users in companies like Apple, Google, Amazon, Twitter, and Ebay get the most out of Git.
Just like with Tower, our mission with this platform is to help people become better professionals.
That's why we provide our guides, videos, and cheat sheets (about version control with Git and lots of other topics) for free.