
git add
The "add" command marks changes to be included in the next commit.
It adds changes to Git's "Staging Area", the contents of which can then be wrapped up in a new revision with the "git commit" command.
Important Options
<file-path>
Specifies the files you want to add to the Staging Area. Note that you can both enter multiple file paths as well as paths to directories (the latter will then add all modifications in this directory to the Staging Area).
--all
Adds all modifications to the Staging Area. This includes changed files, deleted files, and new files - anywhere inside the project directory.
-u
Adds all changes to existing files to the Staging Area. This includes changed files and deleted files - but not new files that aren't currently tracked by Git.

The Git Cheat Sheet
No need to remember all those commands and parameters: get our popular "Git Cheat Sheet" - for free!
Usage Examples
You can provide one or multiple paths and thereby add changes in these files to the Staging Area:
git add index.html error.htmlThese changes will then be part of the next commit.
In case you want all current modifications in your project to be added to the Staging Area (including deletions and new files), you can simply use "--all" or "-A":
git add --allTip
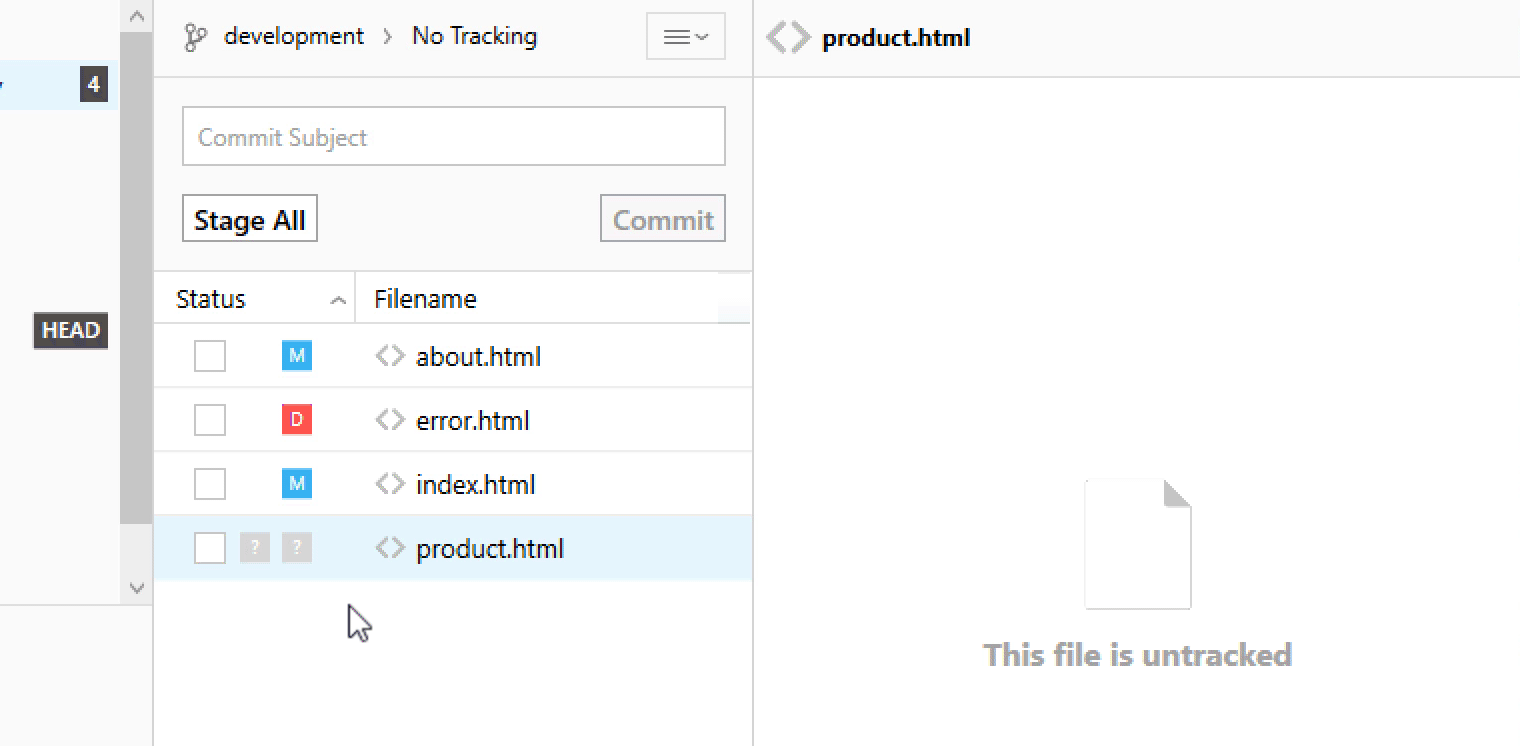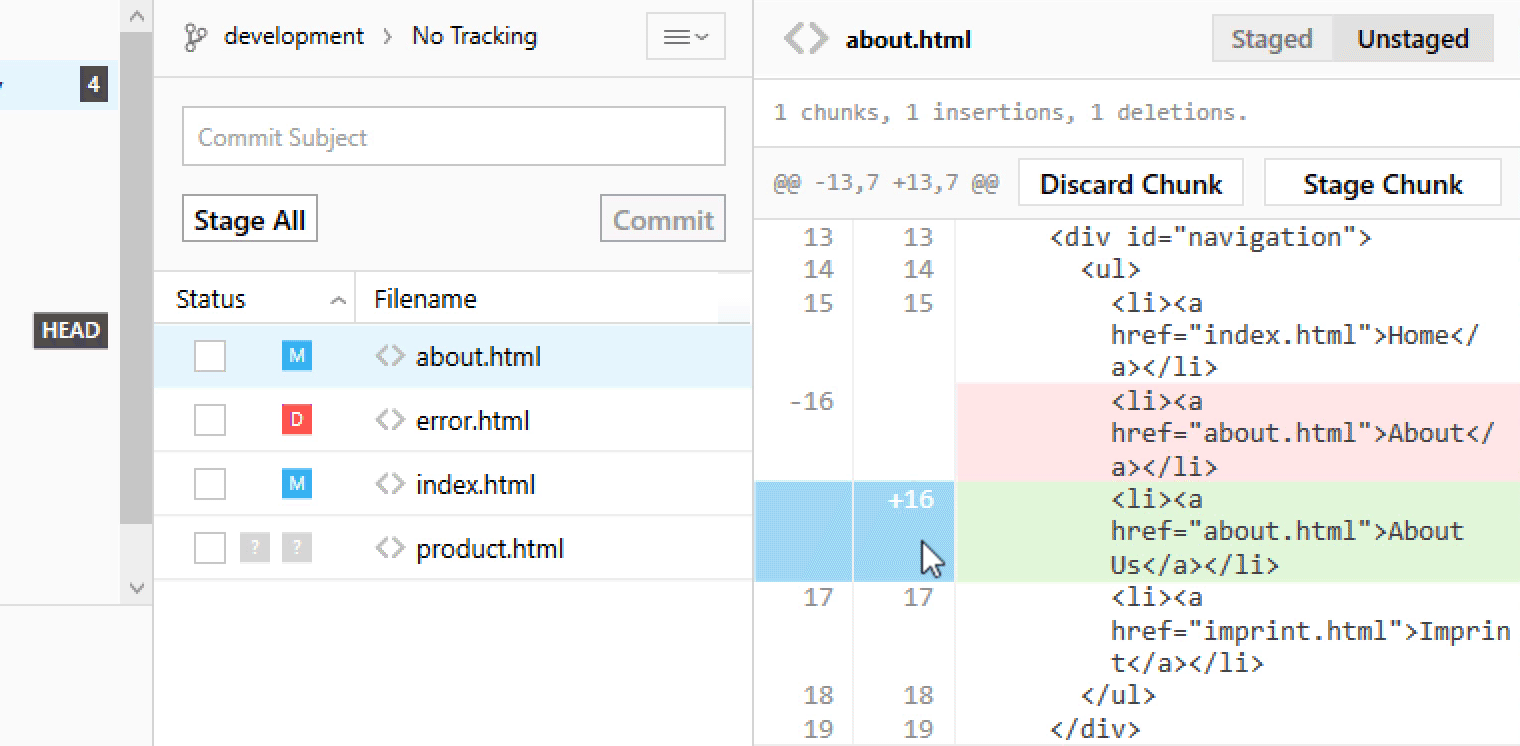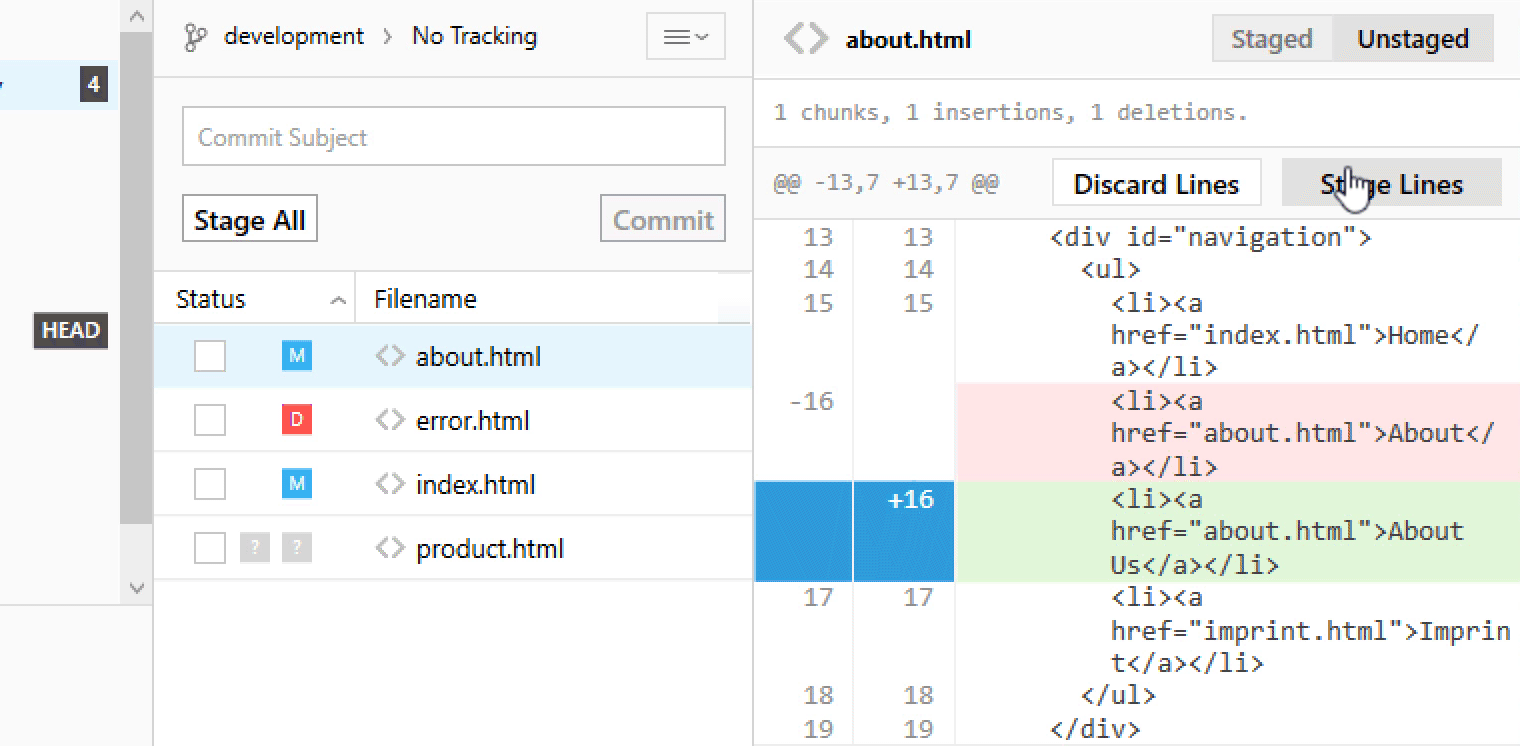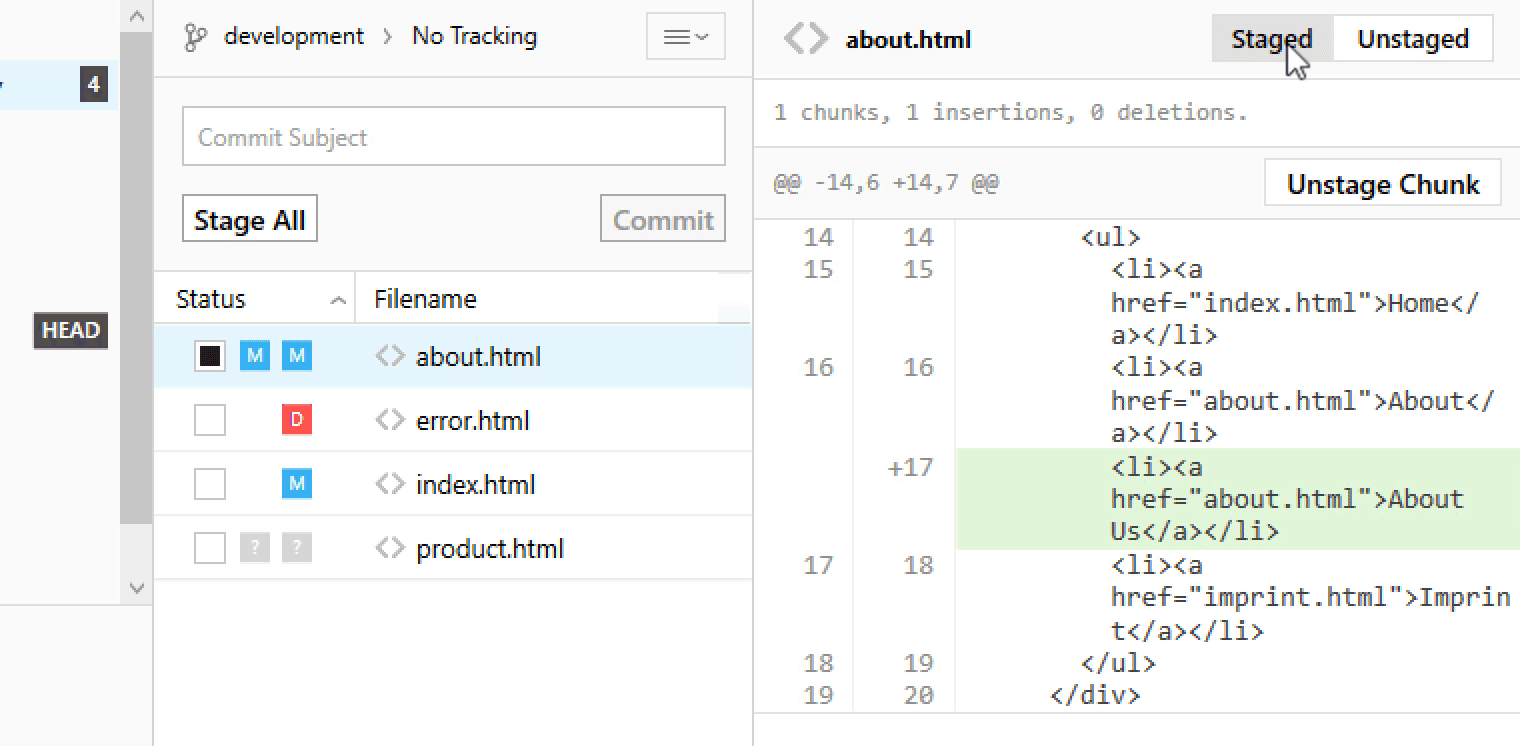
Staging Chunks or Lines of Your Changes
Using the Tower Git client, you can easily select the exact chunks & lines you want to add to the next commit.
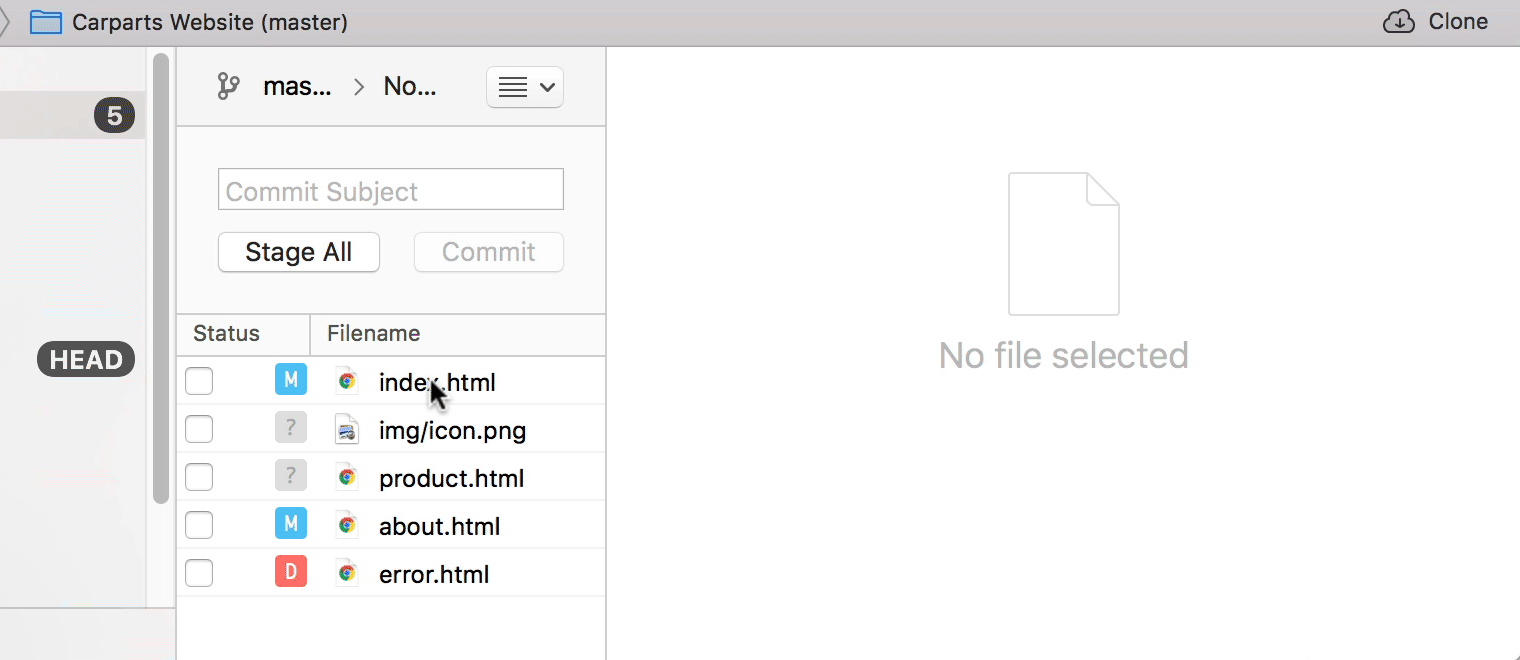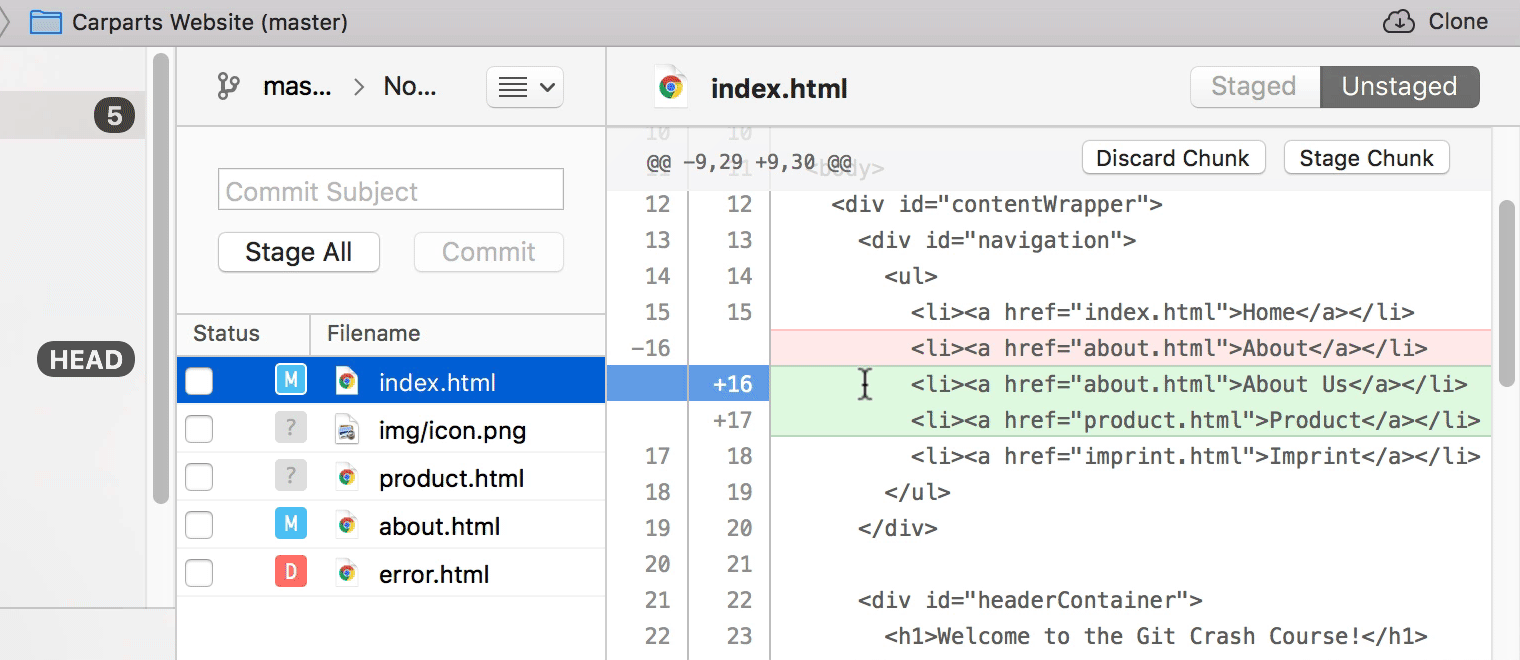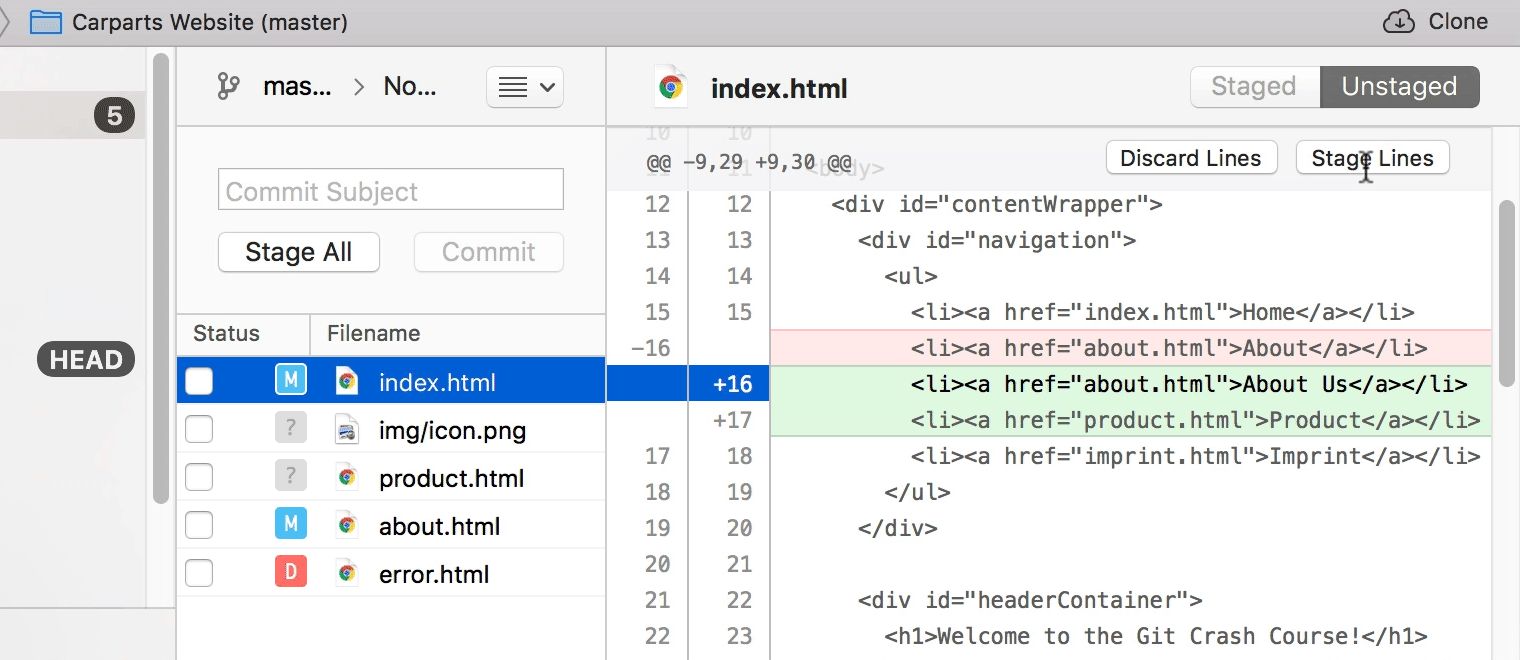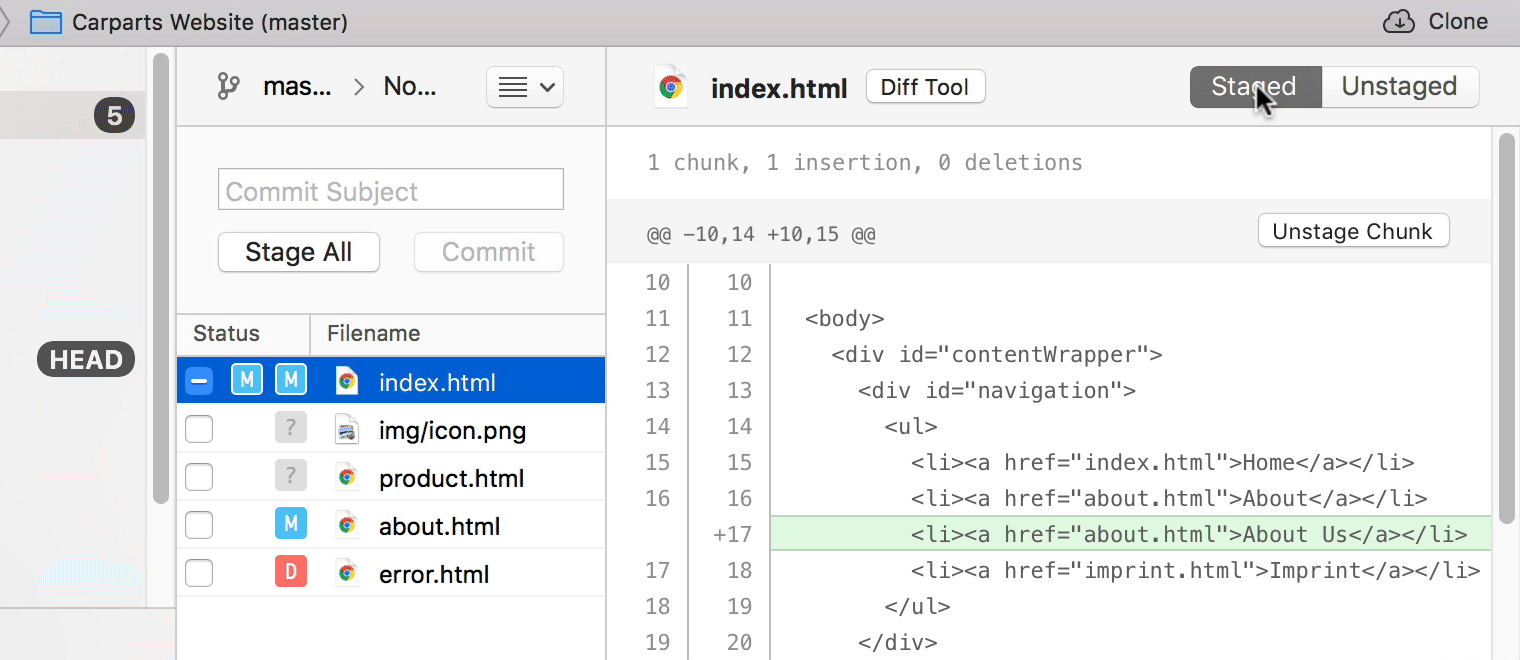
Try it free for 30 days and see why 100,000 developers all over the world use Tower to be more productive with Git!
Learn More
- Check out the chapter Working on Your Project in our free online book
- Find the full command description in the Git documentation
- More frequently asked questions about Git & version control
Get our popular Git Cheat Sheet for free!
You'll find the most important commands on the front and helpful best practice tips on the back. Over 100,000 developers have downloaded it to make Git a little bit easier.

About Us
As the makers of Tower, the best Git client for Mac and Windows, we help over 100,000 users in companies like Apple, Google, Amazon, Twitter, and Ebay get the most out of Git.
Just like with Tower, our mission with this platform is to help people become better professionals.
That's why we provide our guides, videos, and cheat sheets (about version control with Git and lots of other topics) for free.